Sealless Pumps for a Safer and Greener World


Marine pumps play a crucial role in the maritime industry, facilitating a range of operations from ballast management to cargo transfer and bilge water removal. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global marine pumps market is projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for efficient marine operations and sustainable practices within the shipping sector. As vessels become more complex, the need for reliable and high-performance marine pumps has never been more critical.
Renowned marine engineering expert Dr. James Cooley highlights, "The advancement in marine pumps technology is paramount for ensuring the safety and efficiency of naval operations." This statement underscores the integral functions that marine pumps serve aboard various types of vessels, including commercial ships, yachts, and naval fleets. With the diversity in design and application, understanding the different types and functionalities of marine pumps is essential for marine operators aiming to optimize performance and adhere to environmental regulations. As such, a comprehensive examination of marine pumps—encompassing their types, functions, and applications—will provide valuable insights into their significance within the industry.
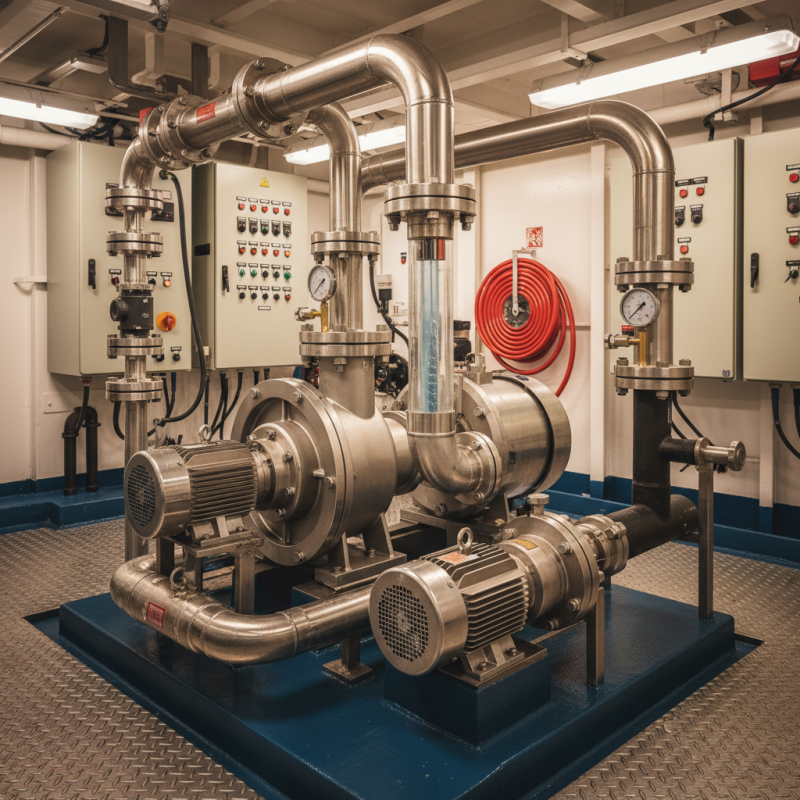

Marine pumps are specialized devices designed to transfer fluids in marine environments, playing a crucial role in various applications related to ships, boats, and offshore platforms. These pumps are engineered to withstand the unique challenges of marine operations, such as corrosive saltwater exposure, high pressure, and the need for reliability in demanding conditions. By facilitating the movement of water, fuel, lubricants, and other liquids, marine pumps ensure the efficient functioning of vessels and marine facilities.
There are several types of marine pumps, each serving distinct functions depending on the specific requirements of the application. Common types include centrifugal pumps, which are widely used for their ability to handle large volumes of water; gear pumps, known for their precision in transferring oil; and diaphragm pumps, which are often used for pumping hazardous materials. The versatility of marine pumps extends across various sectors, including commercial shipping, fishing, oil and gas exploration, and recreational boating, highlighting their importance in ensuring safe and operational marine activities.
Marine pumps are essential components in various maritime applications, serving multiple purposes depending on their design and functionality. Key types of marine pumps include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and submersible pumps. Centrifugal pumps are widely used for transferring fluids due to their efficiency and ability to handle large volumes of liquid. They operate by converting rotational kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy, allowing for effective movement of water, fuel, and other fluids in a marine environment.
Positive displacement pumps, on the other hand, are ideal for applications requiring precise flow rates and high pressures. These pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge outlet, making them suitable for tasks such as ballast systems or bilge pumping.
Submersible pumps are specifically designed to operate underwater, making them crucial for applications like dewatering, sewage pumping, and oil extraction. Their design allows them to be submerged in the fluid they are pumping, ensuring efficiency and ease of use in challenging marine conditions.
Each type of marine pump possesses unique characteristics that cater to the diverse needs of maritime operations.
Marine pumps play a crucial role in various maritime operations, providing essential functions for the efficient and safe transportation of goods and services at sea. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global marine pump market is projected to reach USD 3.09 billion by 2025, reflecting the increasing demand for maritime infrastructure and vessel performance. Among their key functions, marine pumps facilitate ballast water management, ensuring ships maintain stability and safety during transit. This is particularly vital as regulations surrounding ballast water treatment become stricter, requiring effective pump systems to manage compliance without compromising operational efficiency.
In addition to ballast water management, marine pumps are integral to cargo handling operations. They assist in the transfer and management of liquid cargoes, significantly impacting operational speed and efficiency. For instance, in the case of oil tankers, pumps are responsible for loading and discharging large quantities of oil, which can range from 5,000 to over 500,000 barrels per trip. With a growing focus on sustainability in the maritime industry, the adoption of advanced pump technologies that minimize spillage and environmental impact is becoming increasingly critical, driven by both regulatory requirements and public expectations. As the dynamics of maritime operations evolve, the importance of marine pumps in maintaining productivity and environmental compliance will continue to grow.
Marine pumps play a crucial role in various marine environments, significantly impacting operational efficiency and safety. They are designed to manage the movement of fluids, whether it be for ballast, cargo transfer, or wastewater management. According to a recent report by Markets and Markets, the global marine pumping market is projected to reach USD 4.6 billion by 2025, driven by the growing maritime trade and the need for efficient fluid management solutions.
In the shipping industry, marine pumps are essential for ballast water treatment systems, which help maintain vessel stability and prevent the transfer of invasive species. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has mandated regulations that require ships to manage ballast water effectively, thereby increasing the demand for specialized pumps. These pumps also find extensive applications in cooling systems for engine compartments, ensuring optimal performance and safety during voyages. Reports indicate that more than 60% of marine accidents are related to equipment failure, highlighting the importance of reliable marine pump systems in preventing such incidents.
In offshore operations, marine pumps are utilized for oil and gas extraction, where they manage the transfer of crude oil and other fluids from subsea wells to surface facilities. As the oil and gas industry seeks to enhance production efficiency, the necessity for advanced pumping solutions becomes evident. Additionally, the renewable energy sector, particularly in offshore wind farms, has begun to adopt marine pumps for various applications, including hydraulic actuation systems. This versatility underscores the vital role of marine pumps across different marine environments, ultimately contributing to sustainable practices in the maritime industry.
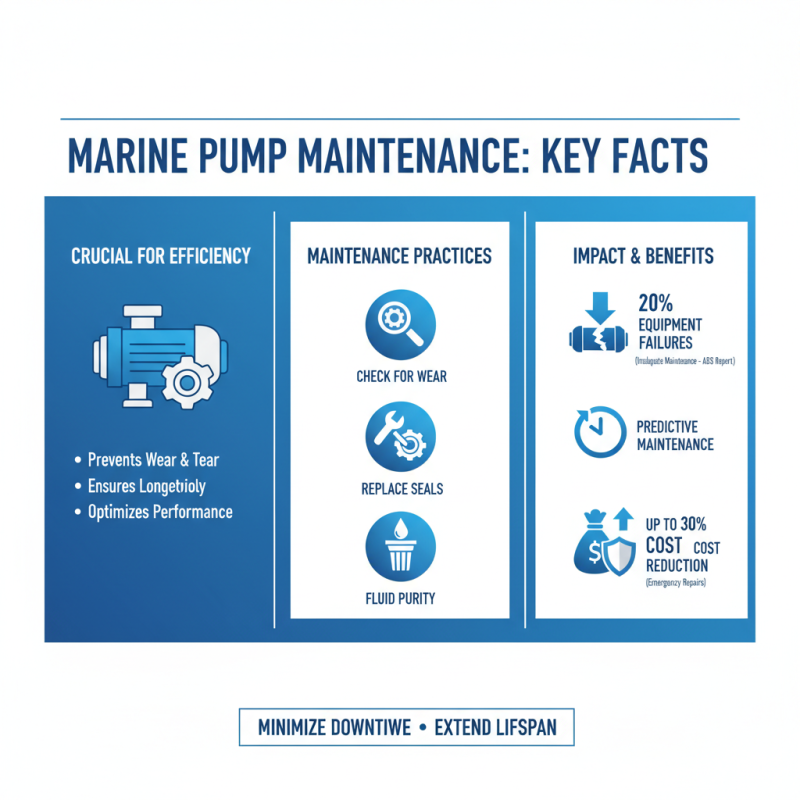
Maintaining marine pumps is crucial for ensuring their operational efficiency and longevity. Regular maintenance practices generally involve checking for wear and tear, replacing worn-out seals, and ensuring that fluids are free of contaminants. According to a report by the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS), nearly 20% of marine equipment failures can be attributed to inadequate maintenance, underscoring the importance of adherence to a regular maintenance schedule. Implementing a predictive maintenance program can not only minimize downtime but also extend the lifespan of marine pumps, potentially reducing costs related to emergency repairs by up to 30%.
To enhance marine pump efficiency, operators can incorporate best practices such as monitoring vibration levels and fluid pressure. Data from the International Maritime Organization (IMO) suggests that optimally maintained pumps can improve system efficiency by up to 15%, allowing for better fuel consumption and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, utilizing technology like condition monitoring systems can provide real-time data, enabling operators to detect anomalies early. This proactive approach not only assures performance but also complies with growing regulatory demands for greener marine operations, which aim to lower emissions and ensure sustainable marine practices.





